How to update VMware Windows VM’s DNS using PowerCLI
This post will show you how to update a VMware Windows virtual machine’s DNS IP addresses using PowerCLI.
You’ll also see how I went from a starting point to a fully working script – all thanks to the awesome #vCommunity!
Here at work we’ve been doing a number of networking, AD, and DNS changes. In doing so, our DNS IP address have changed. Changing the DNS settings for our workstations was easy, simply edit the DHCP scope.
The servers on the other hand all had static IP’s and static DNS IP’s entered, each of which needed to be updated.
Just like anyone else who uses PowerCLI – the first thing I did was search Google for any code that is already available.
One of the first results I found was this blog post from @jasemccarty
After a few minor edits I had this code ready to run.
Update VMware Windows VM’s DNS using PowerCLI Take 1
# Jase McCarty 6/6/2010
Connect-VIServer vcenter.jasemccarty.com
$HostCred = $Host.UI.PromptForCredential("Please enter credentials", "Enter ESX host credential", "", "")
$GuestCred = $Host.UI.PromptForCredential("Please enter credentials", "Enter Guest credentials", "", "")
$vmlist = Get-Content C:\Scripts\serverlist.txt
foreach ($item in $vmlist) {
# I like to map out my variables
#$vmname = $item.vmname
$pdnswins = "192.168.1.1"
$sdnswins = "192.168.1.2"
#Get the current interface info
$GuestInterface = Get-VMGuestNetworkInterface -VM $vmlist -HostCredential $HostCred -GuestCredential $GuestCred
#If the IP in the VM matches, then I don't need to update
Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface -VMGuestNetworkInterface $GuestInterface -HostCredential $HostCred -GuestCredential $GuestCred -DNS $pdnswins,$sdnswins
}
The script however failed. Instead I was presented with red text about missing commands.
At first I searched Google again for “Get-VMGuestNetworkInterface” and found a vSphere PowerCLI Reference page and everything looked good to me.
I reached out to Jase via Twitter to see if he had any suggestions.
Almost immediately Jase kindly informs me that those cmdlet’s have been deprecated, along with a link to this announcement and this Microsoft blog post.
Great, I have everything I need to update the script!
But Jase isn’t done yet. Moments later I get another message from Jase, this time to a Github page with another script he just put together:
Update VMware Windows VM’s DNS using PowerCLI Take 2!
Function Set-VMGuestWindowsIp {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This function is a modification the Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface
.DESCRIPTION
This function is a modification the Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface
.PARAMETER VM
The VM
.PARAMETER Adapter
The Name of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER IP
The IP of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER Netmask
The Netmask of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER Gateway
The Gateway of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER GuestUser
The Windows Guest User Account
.PARAMETER GuestPass
The Windows Guest User Account Password
.PARAMETER SetDns
True or False, set the DNS Address to the Hardcoded DNS
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter "Local Network Connection" -GuestUser "admin" -GuestPass "pass" -SetDns $true
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter "Local Network Connection" -GuestUser "admin" -GuestPass "pass" -SetDns $true -IP "192.168.0.5" -Netmask "255.255.255.0" -Gateway "192.168.0.1"
.NOTES
Author : Jase McCarty
Version : 0.1
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$VM,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$Adapter,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$IP,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Netmask,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Gateway,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestUser,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestPass,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][Boolean]$SetDns
)
# Windows netsh path
$netshPath = "C:\Windows\System32\netsh.exe"
# Set DNS Entries
$pdns = "1.1.1.1"
$sdns = "8.8.8.8"
$netsh = "$netshPath interface ip set address $Adapter static $IP $NetMask $Gateway1"
$netsh1 = "$netshPath interface ip set dnsserver $Adapter static $pdns"
$netsh2 = "$netshPath interface ip set dnsserver $Adapter static $sdns Index=2"
If ($IP) {
# Set the IP Address
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType bat -ScriptText $netsh
}
If ($SetDns -eq $true) {
# Set the Primary DNS
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType bat -ScriptText $netsh1
# Set the Secondary DNS
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType bat -ScriptText $netsh2
}
}
# Windows Path
#$vmlist = Get-Content C:\Scripts\logs\serverlist.txt
# Path on my Mac
$vmList = Get-Content /Users/jase/PowerCLI/serverlist.txt
foreach ($VM in $vmlist) {
Set-VMGuestWindowsIp -VM $VM -Adapter "Local Area Connection" -GuestUser "admin" -GuestPass "pass" -SetDns $true
}
I was shocked. I wasn’t expecting anything close to this much feedback. Just a pointer in the right direction and instead get a nearly fully blown working script.
I tried it and received a number of syntax errors. Now to be fair Jase did warn me that he didn’t have any Windows machines to test it on.
Time for more debugging.
How to update VMware Windows VM’s DNS using PowerCLI – Works!
There was three things that I modified in the above code:
- I found I didn’t need to provide the full path to netsh.exe so I removed that variable and replaced it simply with netsh.
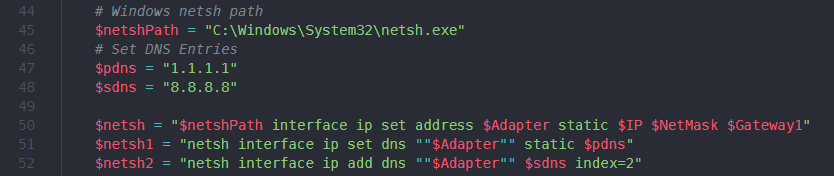
- The $Adapter variable in both of the netsh1 & netsh2 (lines 51-52) needed to be in double quotes.
- I needed to use “netsh interface ip add dns “”$Adapter”” $sdns index=2″ in $netsh2 (line 52) in order for the second DNS IP to be properly configured.
Below is the final version of the script.
Function Set-VMGuestWindowsIp {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This function is a modification the Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface
.DESCRIPTION
This function is a modification the Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface
.PARAMETER VM
The VM
.PARAMETER Adapter
The Name of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER IP
The IP of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER Netmask
The Netmask of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER Gateway
The Gateway of the Windows Network Adapter
.PARAMETER GuestUser
The Windows Guest User Account
.PARAMETER GuestPass
The Windows Guest User Account Password
.PARAMETER SetDns
True or False, set the DNS Address to the Hardcoded DNS
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter "Local Network Connection" -GuestUser "admin" -GuestPass "pass" -SetDns $true
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter "Local Network Connection" -GuestUser "admin" -GuestPass "pass" -SetDns $true -IP "192.168.0.5" -Netmask "255.255.255.0" -Gateway "192.168.0.1"
.NOTES
Author : Jase McCarty
Version : 0.1
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$VM,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$Adapter,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$IP,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Netmask,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Gateway,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestUser,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestPass,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][Boolean]$SetDns
)
# Windows netsh path
$netshPath = "C:\Windows\System32\netsh.exe"
# Set DNS Entries
$pdns = "1.1.1.1"
$sdns = "8.8.8.8"
$netsh = "$netshPath interface ip set address $Adapter static $IP $NetMask $Gateway1"
$netsh1 = "netsh interface ip set dns ""$Adapter"" static $pdns"
$netsh2 = "netsh interface ip add dns ""$Adapter"" $sdns index=2"
If ($IP) {
# Set the IP Address
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType Bat -ScriptText $netsh
}
If ($SetDns -eq $true) {
# Set the Primary DNS
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType Bat -ScriptText $netsh1
# Set the Secondary DNS
Invoke-VMScript -VM (Get-VM -Name $VM) -GuestUser $GuestUser -GuestPassword $GuestPass -ScriptType Bat -ScriptText $netsh2
}
}
# Windows path to server list
$vmlist = Get-Content C:\Scripts\logs\serverlist.txt
# Mac path to server list
# $vmList = Get-Content /Users/jase/PowerCLI/serverlist.txt
foreach ($VM in $vmlist) {
Set-VMGuestWindowsIp -VM $VM -Adapter "Ethernet0" -GuestUser "domain\admin" -GuestPass "Password123" -SetDns $true
}
I take no credit for this code. This was made possible by Jase and his generosity by going above and beyond.
The #vCommunity has always been an incredibly helpful community and it’s guys like @jasemccarty that make it what it is!
Thanks for all the work you put into this. I have been using straight PowerShell to update dns on my servers relying on Get-WMIObject Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration. I like this more elegant solution for my vm servers. I will still need to rely on Get-WMIObject to change my physical Windows servers.
Just another thought if you wanted for this to be more automated, since you need to know the name of the network adapter in windows to be able to target it, you can have the script look for it before you make the changes using something like this.
$Network = Invoke-VMScript -VM $VMName -ScriptType Powershell -ScriptText`
“(gwmi Win32_NetworkAdapter -filter ‘netconnectionid is not null’).netconnectionid”`
-GuestUser “UserName” -GuestPassword “Password”
$NetworkName = $Network.ScriptOutput
$NetworkName = $NetworkName.Trim()
Where $NetworkName would be the Windows name of the adapter just in case that all of your adapter names are different depending of the version of the OS.
Stuart you rock buddy. Great addition and I can see this being very handy for those environments where the network adapter names are all over the place.
Thanks for sharing!
Invoke-VMScript is pretty slow for me, I’d add a -RunAsync switch, and requery the VM fewer times:
Function Set-VMGuestWindowsIp {
UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter “Local Network Connection” -GuestUser “admin” -GuestPass “pass” -SetDns $true
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> UpdateIp.ps1 -VM VMNAME -Adapter “Local Network Connection” -GuestUser “admin” -GuestPass “pass” -SetDns $true -IP “192.168.0.5” -Netmask “255.255.255.0” -Gateway “192.168.0.1”
.NOTES
Author : Jase McCarty
Version : 0.1
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$VM,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$Adapter,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$IP,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Netmask,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][String]$Gateway,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestUser,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][String]$GuestPass,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][Boolean]$SetDns,
[switch]$RunAsync
)
# Windows netsh path
$netshPath = “C:\Windows\System32\netsh.exe”
# Set DNS Entries
$pdns = “1.1.1.1”
$sdns = “8.8.8.8”
$netsh = “$netshPath interface ip set address $Adapter static $IP $NetMask $Gateway1”
$netsh1 = “netsh interface ip set dns “”$Adapter”” static $pdns”
$netsh2 = “netsh interface ip add dns “”$Adapter”” $sdns index=2″
$invokeParam = @{
VM = Get-VM -Name $VM
GuestUser = $GuestUser
GuestPass = $GuestPass
ScriptType = ‘Bat’
RunAsync = $RunAsync.IsPresent
}
If ($IP) {
# Set the IP Address
Invoke-VMScript @invokeParam -ScriptText $netsh
}
If ($SetDns -eq $true) {
# Set the Primary DNS
Invoke-VMScript @invokeParam -ScriptText $netsh1
# Set the Secondary DNS
Invoke-VMScript @invokeParam -ScriptText $netsh2
}
}